Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked a vigorous debate among nutrition experts, especially as sugar addiction and sugar cravings become more prevalent in our daily lives. While many people argue that the health effects of sugar mimic those found in addictive substances, it’s essential to approach this topic with nuance. Processed foods and sugar often combine to create irresistibly palatable products that can lead to habitual consumption, possibly resulting in withdrawal-like symptoms when reduced drastically. Understanding the actual impact of sugar on our bodies and minds can be a vital step toward reducing sugar intake and promoting healthier lifestyles.
The exploration of sugar’s impact on health is crucial as we consider the implications of sweeteners on our diets. Often referred to as a potential source of addiction, sugar generates significant cravings that may rival those associated with more notorious substances. In our highly processed food environment, the balance between enjoyment and health becomes increasingly challenged, making it vital to recognize the need for moderation. This complex relationship between humans and sweetness necessitates a closer look at not only our dietary choices but also the psychological factors at play. By examining these alternative terms and concepts surrounding sugar and its consumption, we can better navigate our journey toward healthier eating habits.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
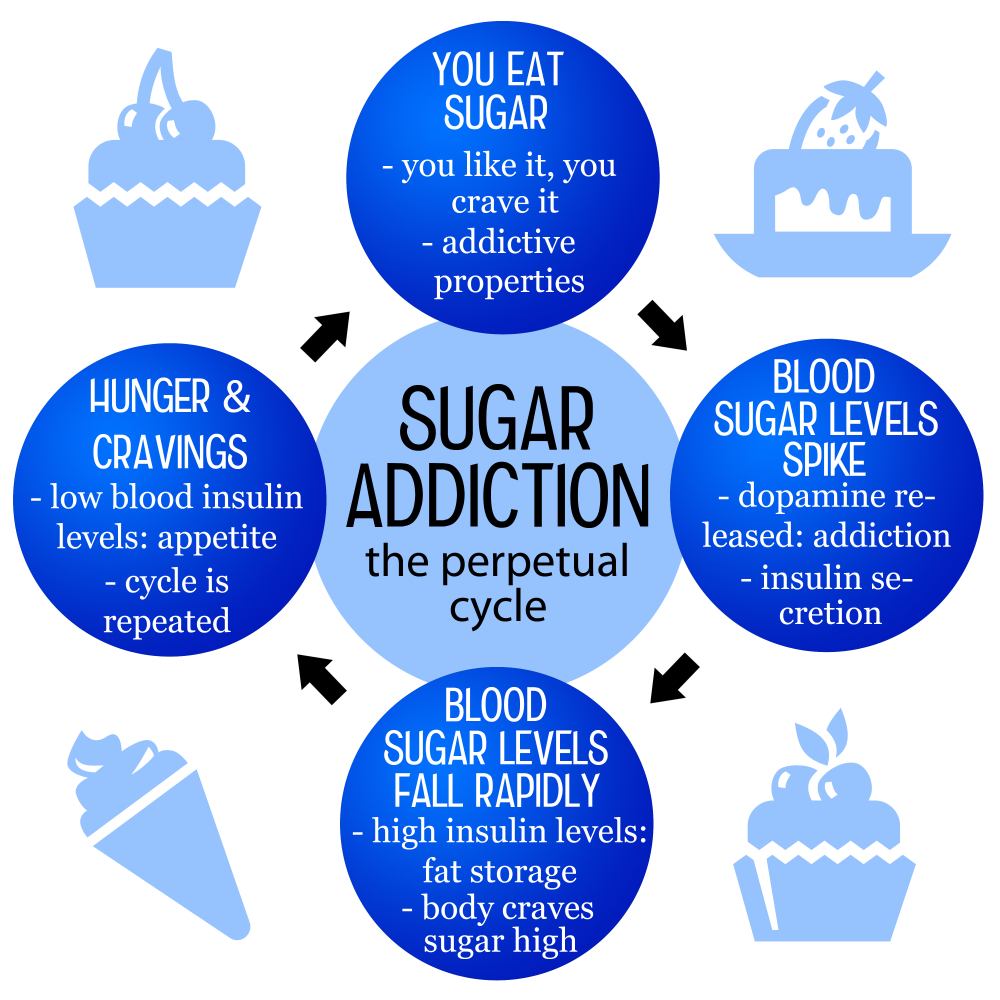
Sugar addiction is a term that frequently enters discussions about dietary habits and health. While sugar does not fit the strict clinical definitions of an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, it does induce cravings that can lead to compulsive behaviors. Research shows that excessive sugar intake activates brain pathways similar to those triggered by addictive drugs, creating a rewarding experience that many find hard to resist. This can lead to a cycle of overconsumption, where individuals feel compelled to seek out sweets and processed foods, resulting in habitual sugar intake.
Moreover, the proliferation of ultra-processed foods in our diet exacerbates the problem. These foods are not only high in sugar, but often include unhealthy fats and salts, making them even more appealing. As people consume these hyper-palatable products, they may experience withdrawal-like symptoms when they attempt to reduce their sugar intake, such as irritability and physical discomfort. Understanding the underlying effects of sugar on the brain can help individuals recognize their cravings and approach their diet more mindfully.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like alcohol or nicotine?
While sugar can cause cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. The physical and psychological effects associated with sugar consumption can resemble withdrawal symptoms when consumption stops, but they tend to be less severe. It is vital to distinguish between necessary dietary sugars found in fruits and whole foods and added sugars in processed foods.
What are the health effects of sugar addiction?
Sugar addiction can lead to increased cravings and compulsive eating patterns, contributing to health issues like obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. High sugar intake, particularly from processed foods, can create a cycle of overconsumption, which can negatively impact overall health. Moderation is key to avoiding the adverse health effects associated with sugar.
How can I reduce sugar cravings effectively?
To effectively reduce sugar cravings, consider a gradual decrease in sugar intake rather than an abrupt stop. This can help mitigate withdrawal-like symptoms. Incorporating more whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can also satisfy sweet cravings in a healthier way. Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet can further support reduced cravings for sugar.
Are processed foods the main cause of sugar addiction?
Processed foods often contain high levels of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, making them extremely palatable and easy to overconsume. This can lead to habitual sugar cravings and increased consumption, contributing to what some may describe as sugar addiction. Being mindful of processed food intake and reading labels can help manage sugar consumption effectively.
What is the recommended sugar intake to prevent sugar addiction?
The American Heart Association recommends no more than 9 teaspoons of added sugar for men and 6 teaspoons for women daily. Keeping sugar intake within these guidelines can help prevent the development of sugar cravings and reduce the risk of associated health issues. Staying aware of sugar consumption can promote better dietary habits.
Can eliminating sugar completely help with cravings?
Going cold turkey on sugar can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms, making cravings worse for some. Instead of complete elimination, a gradual reduction in added sugars while focusing on nutritious alternatives may be more sustainable for managing sugar cravings and maintaining a balanced diet.
Does sugar addiction affect mental health?
Excessive sugar consumption can lead to fluctuations in energy levels and mood, potentially impacting mental health. The effects of processed foods, high in added sugars, may contribute to feelings of anxiety and irritability. Moderating sugar intake can have positive effects on overall mental well-being.
Why is sugar considered a ‘gateway’ substance?
Sugar is sometimes referred to as a ‘gateway’ substance because its consumption can lead to cravings for more addictive foods and substances. The habitual intake of sweetened processed foods can create a cycle of increased cravings, making it harder to control intake. Understanding this relationship can aid in making healthier food choices.
How does sugar affect the brain?
Sugar can trigger the reward centers in the brain, similar to how addictive substances do, which can lead to a cycle of cravings and consumption. This reward response can make it challenging to reduce sugar intake. Awareness of this neurological response can help individuals better navigate their eating habits.
Is it possible to enjoy sugar in moderation without becoming addicted?
Yes, enjoying sugar in moderation is not only possible but can also be beneficial. Including small amounts of added sugars in a balanced diet, alongside whole foods, can satisfy cravings without leading to significant health issues or addictive behaviors. The key is to maintain moderation and be mindful of sugar sources.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Sugar and Addiction | Although sugar can increase cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. |
| Physical and Psychological Effects | People can experience withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches and anxiety when they stop consuming sugar, but these symptoms are less severe compared to those from addictive drugs. |
| Need for Sugar | Sugar is necessary in moderation as it is found in many healthy foods like fruits and whole grains. It enhances flavor and can bring pleasure. |
| Consumption Statistics | The average American consumes almost 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, significantly higher than the recommended limits. |
| Gradual Reduction | Instead of eliminating sugar completely, a gradual reduction is advised to avoid withdrawal symptoms. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked considerable debate among nutrition experts. While sugar does have some addictive qualities that can lead to cravings, it is not officially categorized as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. The physiological and psychological effects of sugar consumption can resemble addiction, especially with high levels found in ultra-processed foods. However, understanding sugar’s role as a necessary component of a balanced diet, when consumed in moderation, is essential. The reality is that sugar can enhance our lives when included in reasonable portions, making it crucial to be aware of our intake rather than completely eliminating it.