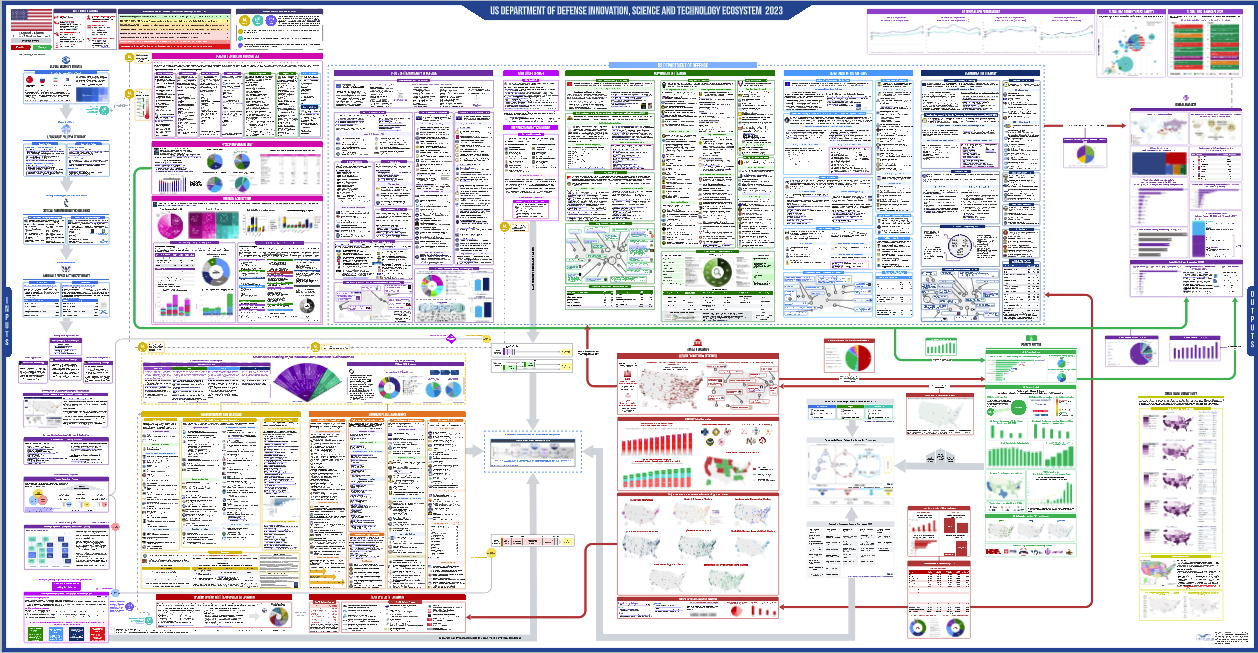
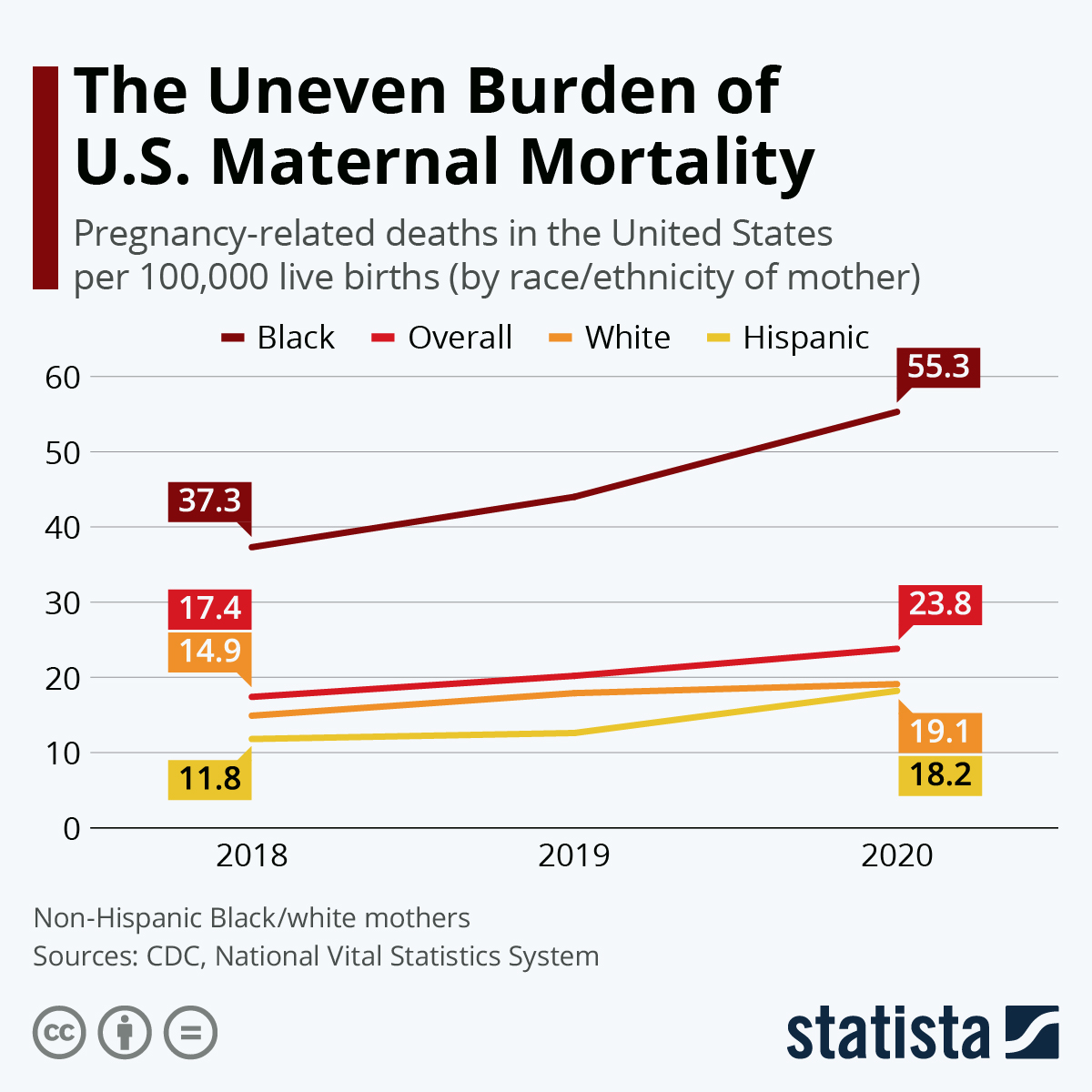
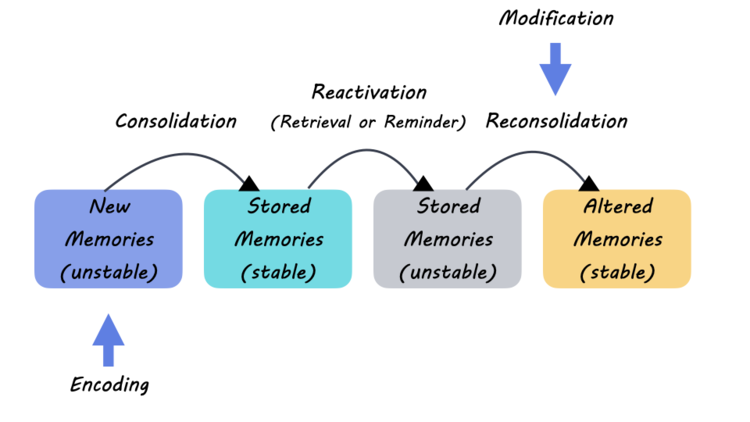
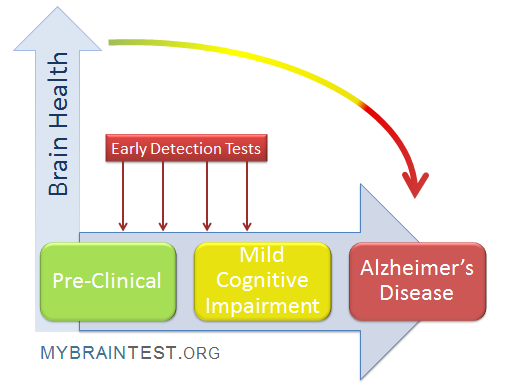
The U.S. innovation ecosystem stands as a shining example of ingenuity, collaboration, and resilience, continually evolving since its inception during World War II. This dynamic landscape, fueled by significant public-private partnerships, has catalyzed groundbreaking advancements in biomedical research and drug development, transforming health outcomes for millions. However, recent NIH funding cuts have raised concerns regarding the sustainability of this ecosystem, threatening the future of vital research initiatives. The collaborative effort that began in wartime with the mass production of penicillin paved the way for a robust structure that has since inspired innovation worldwide. As we delve deeper into the implications of these changes, understanding the history and challenges of the U.S. innovation ecosystem becomes increasingly vital.
The innovation environment in the United States is a rich tapestry of research institutions, government agencies, and private enterprises working in concert to achieve scientific progress. This collaborative network fosters advancements in various fields, particularly in biomedicine, where breakthroughs in treatment and technology have significantly improved public health. With historical roots tracing back to wartime exigencies, the framework for today’s dynamic research climate was established through essential partnerships and funding mechanisms. The ongoing debate surrounding fiscal cuts to research funding necessitates a closer examination of these vital interconnections, especially as we strive to sustain the momentum of historical achievements like the development of antibiotics. Recognizing the interconnectedness of different sectors in this landscape is crucial for ensuring continued advancements and effective responses to future health challenges.
The Origins of the U.S. Innovation Ecosystem
The U.S. innovation ecosystem traces its roots back to the urgency of World War II, when the federal government recognized the critical need for advancements in technology and health. Collaborations between government entities, universities, and private sectors were established, leading to groundbreaking developments such as the mass production of penicillin. This wartime collaboration not only aimed to equip the military with better health solutions but also set a precedent for public-private partnerships that continue to drive innovation today.
Before World War II, U.S. biomedical research was rudimentary at best, marked by a lack of coordination and funding. However, through the efforts of the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD), the partnership model was refined, laying the groundwork for future advancements. The mobilization of civilian scientists created an environment ripe for innovative research, facilitating developments that not only served the war effort but also paved the way for post-war biomedical research.
Public-Private Partnerships in Biomedical Research
Public-private partnerships have become essential pillars of the U.S. innovation ecosystem, particularly in biomedical research. These collaborations allow for the pooling of resources, knowledge, and expertise from both public institutions and private companies, enabling faster and more effective drug development advancements. As federal funding for research has faced scrutiny and potential cuts, these partnerships have been credited with driving innovation through shared investments in technology and research initiatives.
The balance of responsibility and risk between public agencies, such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and private enterprises underlines the importance of sustained funding for these collaborations. The NIH has historically played a vital role in supporting medical research, but recent proposed funding cuts raise concerns about the future of public-private partnerships. Maintaining robust federal funding is crucial for ensuring that these collaborations can continue to thrive and produce groundbreaking results in healthcare.
Impact of NIH Funding on Drug Development
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) funding has significantly shaped the landscape of biomedical research and drug development in the United States. With grants supporting innovative research projects, the NIH has historically been the backbone of scientific exploration, enabling researchers to pursue groundbreaking work that leads to the creation of new therapies. However, recent discussions regarding potential NIH funding cuts have sparked debates about the future sustainability of drug research initiatives.
Without adequate funding, the implications for drug development advancements could be profound. Many pharmaceutical companies depend on the foundational research funded by the NIH to fuel their own drug discovery processes. As these private companies build on publicly funded research findings, any reduction in NIH support could ultimately delay or hinder the development of essential drug therapies, impacting public health outcomes across the nation.
The Legacy of World War II Research
The impact of World War II on American research practices is notable and serves as a reminder of the crucial role government investment can play in fostering innovation. During the war, the urgent need for advancements in healthcare led to an accelerated focus on scientific research and collaboration among the federal government, universities, and private industry. The successful production of penicillin exemplified a significant medical breakthrough that paved the way for modern antibiotic therapies.
This wartime effort created a foundational shift in how the U.S. approached scientific research, leading to the establishment of formal structures for funding and collaboration. Researchers learned the importance of rapid development and response to immediate medical needs, which ultimately shaped the nation’s pursuit of advanced biomedical research techniques for decades to follow.
Challenges Facing the U.S. Innovation Ecosystem Today
Despite the successes of the U.S. innovation ecosystem, challenges persist that threaten its viability. The rising concerns over NIH funding cuts and shifting political priorities create an unstable environment for public-private partnerships that are essential for advancing biomedical research. Economic uncertainty can lead to decreased investments from both public institutions and private entities, jeopardizing the breadth of scientific innovation.
In this context, engaging academia and industry in dialogue about sustainable funding mechanisms is imperative for the future of U.S. innovation. The lessons learned from World War II demonstrate that a proactive approach to public-private collaboration can yield significant returns in health and technology, and today’s stakeholders must advocate for continued partnerships to safeguard the advancements made in biomedicine.
The Role of Academia in Shaping Innovation
Academia plays a vital role in shaping the U.S. innovation ecosystem by fostering research that not only addresses scientific questions but also meets societal needs. Universities have become key players in public-private partnerships, leveraging federal funding to drive projects that lead to significant advancements in biomedical research. Through collaborative initiatives with private firms, academic institutions can translate basic research into practical applications, significantly contributing to drug development and medical solutions.
Moreover, the training environment within universities ensures a steady supply of skilled scientists who are equipped to tackle the challenges of modern biomedical research. By nurturing innovative ideas and fostering entrepreneurial spirit, academia remains a driving force behind the United States’ leadership in healthcare and technology. As the landscape evolves, academic institutions must continue to adapt and collaborate with industry to maintain their position as catalysts for innovation.
Innovation and Economic Growth in the U.S.
The connection between innovation and economic growth is undeniably strong within the context of the U.S. innovation ecosystem. The advancements achieved through public-private partnerships in biomedical research have not only improved health outcomes but also contributed significantly to economic prosperity. Breakthroughs in drug development can lead to new markets, job creation, and economic expansion, demonstrating the intrinsic value of investing in research and development.
As the world increasingly looks to the U.S. as a model for fostering innovation, the need to protect and promote the synergy between federal funding, private initiative, and academic research has never been more critical. Ensuring that policies enhance rather than hinder innovation is essential for maintaining the economic dynamism that arises from substantial biomedical advancements and the growth of the life sciences sector.
Looking to the Future of Biomedical Innovation
As we look to the future, the challenges and opportunities facing the U.S. innovation ecosystem in biomedical research are ever-evolving. Continued collaboration between governmental entities, private industry, and academic institutions will be crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in global healthcare. Policymakers must prioritize the support of research funding and incentives for public-private partnerships to ensure that advancements continue to flow from the laboratory to the marketplace.
Furthermore, embracing emerging technologies and new methodologies, such as artificial intelligence and data analytics in drug development, can catalyze significant breakthroughs. The future of biomedical innovation relies on an agile and responsive ecosystem that remains open to change and primed for collaboration, thereby ensuring a healthier future for all.
Sustaining the Success of the U.S. Innovation System
To sustain the success of the U.S. innovation system, particularly within the realm of biomedicine, a commitment to enduring public-private partnerships is essential. This necessitates a holistic approach to research funding that recognizes the diverse contributions made by federal, state, and local entities, alongside private industry. By integrating resources and expertise from multiple sectors, a more robust and resilient innovation ecosystem can emerge.
Moreover, communication and accountability among partners are pivotal in navigating the complexity of funding mechanisms and research objectives. As the innovation landscape continues to shift, particularly in response to societal and technological challenges, the U.S. must remain vigilant in championing collaborative efforts to promote ongoing advancements in health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
How did World War II impact the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
World War II catalyzed significant advancements in the U.S. innovation ecosystem by establishing vital public-private partnerships that united government, universities, and private industry. This collaboration led to breakthroughs like penicillin mass production, showcasing how urgent military needs can drive innovative biomedical research and technology.
What role do public-private partnerships play in the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
Public-private partnerships are a cornerstone of the U.S. innovation ecosystem, facilitating collaboration that enhances biomedical research and technology development. These partnerships allow for shared resources and expertise, leading to significant advancements in drug development and other fields, as evidenced by historical successes during World War II.
What are the implications of NIH funding cuts on the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
NIH funding cuts pose serious threats to the U.S. innovation ecosystem by potentially limiting financial resources for biomedical research. Reduced funding can impede the development of new medical technologies and therapies, jeopardizing the nation’s leadership in global health innovation.
How did the U.S. innovation ecosystem evolve after World War II?
Post-World War II, the U.S. innovation ecosystem evolved through the establishment of a robust framework for biomedical research, significantly bolstered by the lessons learned during the war. This included enhanced collaboration among universities, the life sciences industry, and federal institutions like the NIH, leading to a golden age of drug development.
How is drug development innovation linked to the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
Drug development innovation is deeply intertwined with the U.S. innovation ecosystem, driven by collaborations among academic institutions, the industry, and government funding. The success of antibiotic developments during WWII exemplifies how federal support can lead to groundbreaking advancements in biomedical research and drug production.
What is the historical significance of the NIH in the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
The NIH has played a pivotal role in the U.S. innovation ecosystem, particularly in biomedical research, by providing crucial funding and fostering collaborations with universities and private firms. Established as a more robust entity post-WWII, it has been integral in advancing public health initiatives and drug innovations.
How did military needs shape today’s biomedical research landscape in the U.S.?
Military needs during World War II directly shaped today’s biomedical research landscape in the U.S. by creating an urgent demand for medical innovations, leading to collaborations between government and scientific communities that laid the groundwork for ongoing drug development and health advancements.
What challenges does the U.S. innovation ecosystem face today?
Today, the U.S. innovation ecosystem faces challenges like potential federal funding cuts, particularly affecting biomedical research. Balancing innovation with budget constraints, while maintaining the quality and effectiveness of public-private partnerships, is vital for sustaining advancements in health and technology.
Why are collaborations in the U.S. innovation ecosystem essential for biomedical advancements?
Collaborations in the U.S. innovation ecosystem are essential for biomedical advancements because they leverage diverse expertise and resources from government agencies, academic institutions, and private enterprises. This synergy accelerates research, development, and delivery of medical solutions that address public health needs.
| Key Points |
|---|
| The U.S. innovation ecosystem is world-renowned and began during World War II, with government-supported research leading to breakthroughs like mass-produced penicillin. |
| The partnership between government, academia, and industry was formalized as a response to urgent wartime needs, establishing a collaborative framework for R&D. |
| Federal funding has historically supported academic research, driving private sector development in biomedical science and technology. |
| The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has played a crucial role in funding biomedicine, though recent policies threaten to limit this support. |
| The success of wartime research efforts led to significant advancements in drug development and medical technologies post-war, influencing future generations of scientists. |
| Ongoing public-private research partnerships continue to be pivotal in ensuring the sustainability and growth of the U.S. innovation ecosystem. |
Summary
The U.S. innovation ecosystem is a vital component of global advancements in technology and health. Originating in response to pressing needs during World War II, this collaborative model has flourished, blending government support with private sector innovation. The foundational work accomplished then, particularly in biomedicine, has established a robust framework that empowers continuous growth and evolution in scientific research and technological development. As challenges arise, particularly in funding, it is essential to maintain the integrity of this ecosystem to ensure its future success and global competitiveness.