Suicide prevention for older adults is an urgent and often overlooked public health issue, as this age group faces the highest suicide rates yet has the fewest resources available. Recent research indicates that elderly suicide risk is rising, with significant contributions from factors such as loneliness and social isolation. Geriatric suicide prevention efforts are critical in addressing the unique mental health needs of seniors, who may struggle to find appropriate support. Despite the increasing number of older adults seeking online resources for mental health, accessible information remains scarce. By shining a light on these challenges, we can advocate for enhanced mental health resources for seniors and foster a supportive environment that reduces the alarming rates of suicide in our aging population.
The plight of older individuals grappling with suicidal thoughts represents a significant challenge in contemporary society. Known affectionately as seniors or the elderly, these individuals often experience heightened feelings of isolation, alongside a notable lack of tailored mental health services. The phenomenon of loneliness and its direct correlation to suicide rates in this demographic emphasizes the necessity for targeted interventions. With a considerable proportion of older adults using the internet to seek help, it is crucial to ensure that relevant online resources are readily available and accessible. By acknowledging the nuanced needs of aging individuals, we can develop comprehensive strategies for effective suicide prevention and support.
Understanding the Elderly Suicide Risk
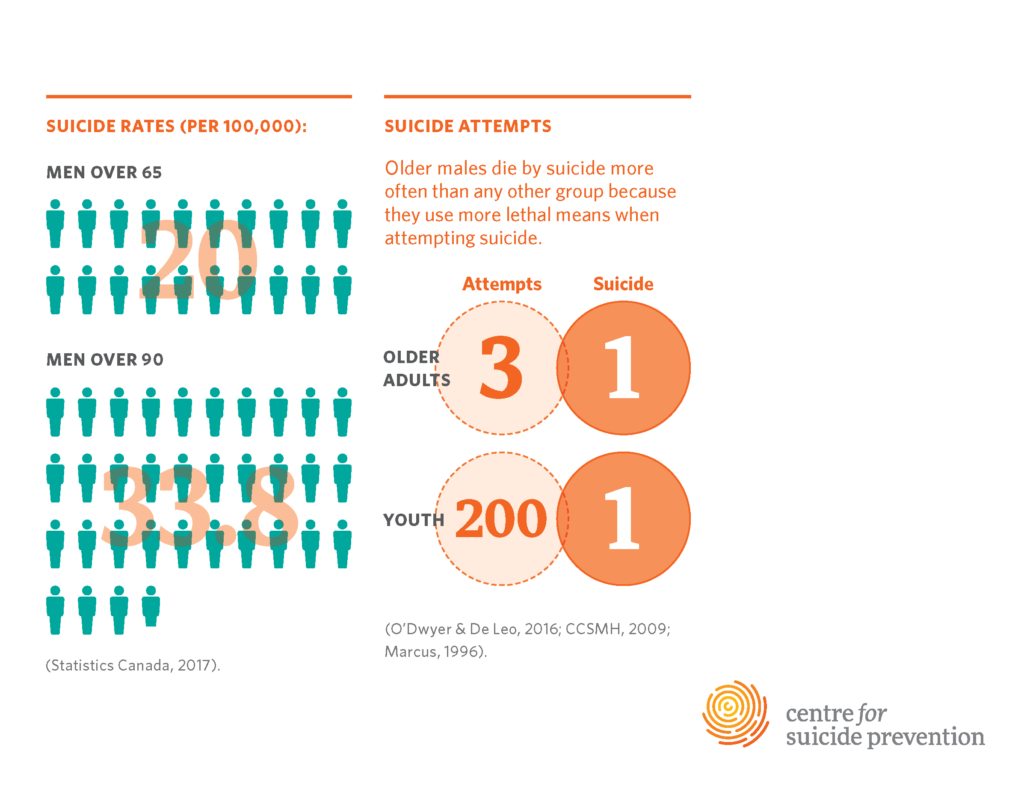
Suicide rates among older adults, particularly those aged 75 and older, are alarmingly high, standing at about 20.3 per 100,000 according to the CDC. This demographic faces unique challenges, including the loss of loved ones, declining health, and increased feelings of loneliness and isolation, all of which can heighten the risk of suicide. Compounding this issue, many older adults often feel unheard or unrepresented in mental health discussions, leading to a concerning gap in available support services tailored specifically for them.
The prevalence of suicidal thoughts among seniors highlights the urgent need for comprehensive mental health resources for seniors. Factors contributing to elderly suicide risk can include physical illnesses, mental disorders such as depression, and social isolation. To effectively decrease these troubling rates, it is essential to create awareness about the specific circumstances that lead to suicidal ideation in older adults, helping to foster empathy and better resource allocation in mental health services.
The Importance of Mental Health Resources for Seniors
As noted by Ipsit Vahia, a leading figure in geriatric psychiatry, there is a significant imbalance in how online suicide prevention resources are targeted. The lack of accessible mental health resources for seniors not only fails to address the specific needs of this demographic but also highlights a systematic oversight in preventing elderly suicide. These resources could range from hotlines tailored for seniors to information on managing mental health issues that impact older adults.
Empowering older adults with the right mental health resources can significantly reduce the risk of suicide. Access to counseling services, online support groups, and educational platforms that focus on mental well-being can make a substantial difference. Importantly, studies show that public-facing suicide prevention campaigns could effectively address these gaps, making tailored campaigns crucial for ensuring that elderly individuals have the support they need.
Geriatric Suicide Prevention Strategies
To combat the rising rates of suicide among older adults, targeted geriatric suicide prevention strategies must be developed. These strategies should revolve around creating age-sensitive programs that recognize the unique challenges faced by seniors. This includes addressing social isolation, which has been strongly linked to increased suicidal thoughts and actions among the elderly. Building a community around seniors, through both physical gatherings and online platforms, can act as a buffer against these feelings of loneliness.
Another key element in geriatric suicide prevention is comprehensive training for healthcare providers. Ensuring that clinicians are equipped with the knowledge and skills to identify signs of distress and suicidal thoughts in older patients will allow for timely intervention. Community education initiatives could further promote awareness and empower seniors, caregivers, and families to seek help early when warning signs emerge.
Online Resources for Older Adults
As older adults increasingly turn to the internet to seek health information, enhancing online resources becomes paramount. Currently, many seniors struggle to find relevant and accessible suicide prevention information tailored specifically to their needs. This highlights the urgency for organizations to invest in digital platforms that are easy to navigate and specifically designed for older users, offering clear pathways to necessary support.
Effective online resources for older adults should include user-friendly websites, mobile apps, and comprehensive database directories for local mental health services. Moreover, integrating suicide prevention within existing health platforms that older adults frequently visit can increase the likelihood of engagement with these resources, thereby reducing barriers and enhancing access to critical support.
Combating Loneliness and Suicide in the Elderly
Loneliness is a significant risk factor for suicide among seniors. As individuals age, they may experience the loss of significant social connections, leading to an increased sense of isolation. Addressing loneliness through community outreach programs and social activities can provide essential social support and connectedness for the elderly, effectively lowering their risk of suicidal ideation.
Additionally, promoting intergenerational relationships can create opportunities for engagement and mutual support between younger and older community members. Encouraging volunteerism and social interactions can help bridge the gaps that often lead to feelings of loneliness, offering older adults a sense of purpose and belonging that is crucial for their mental well-being.
The Role of Healthcare Providers in Suicide Prevention
Healthcare providers play a critical role in identifying and addressing the mental health needs of older adults. It is essential for physicians and caregivers to have awareness and training in recognizing the warning signs of depression and suicidal thoughts among their elderly patients. Implementing routine screening for mental health issues in regular check-ups can facilitate early intervention when risks are detected.
Moreover, healthcare providers must foster open dialogues with their patients regarding mental health. Creating an environment where older adults feel safe to discuss their mental well-being, including thoughts of suicide, is vital. By normalizing these conversations, providers can help destigmatize seeking help and encourage seniors to utilize available mental health resources more actively.
Advocating for Policy Changes in Elderly Mental Health
Advocating for policy changes to enhance mental health resources for older adults is an essential step toward reducing suicide rates in this demographic. Increased funding for mental health programs that focus explicitly on geriatric care is needed to create a more inclusive mental health system. Policymakers must recognize the unique needs of older adults and work to ensure that adequate resources are allocated to address their specific challenges and vulnerabilities.
Furthermore, implementing community-wide initiatives that promote the mental health of older adults can foster support networks that are crucial for preventing suicide. Policies that encourage partnerships between healthcare providers and community organizations can help create comprehensive outreach strategies that cater to the elderly population, leading to improved access to vital mental health services.
The Impact of Social Isolation on Mental Health
Social isolation has profound effects on the mental health of older adults, often resulting in increased feelings of loneliness, despair, and suicidal tendencies. It’s crucial to recognize that many seniors lack meaningful social interactions, which can lead to chronic feelings of loneliness that significantly impact their well-being. Understanding this relationship is vital to developing effective interventions for suicide prevention.
Community initiatives focused on fostering connections among older adults can help combat social isolation. Activities such as group classes, senior centers, and community engagement projects serve as effective platforms for creating social networks. By promoting social engagement, we can vastly improve the mental health landscape for seniors, potentially decreasing suicide rates among this vulnerable group.
Utilizing Technology for Elderly Suicide Prevention
The use of technology in suicide prevention among older adults presents an innovative approach to combat this pressing issue. Given that many seniors are increasingly tech-savvy, utilizing digital platforms for providing mental health resources can enhance their access to critical support. Online therapy sessions, telehealth consultations, and interactive mental health apps can offer immediate assistance and information.
Furthermore, creating online support communities specifically designed for older adults can provide safe spaces for sharing experiences and receiving peer support. These platforms can help bridge the gap created by physical distances, allowing seniors who may feel isolated to connect with others experiencing similar challenges—reaching out for help in a more comfortable setting.
Future Directions in Elderly Suicide Prevention Research
Ongoing research into elderly suicide prevention is essential to identify effectively the most relevant and impactful strategies for this population. More studies focusing on the particular risk factors and barriers to accessing mental health resources will inform the development of targeted interventions aimed at reducing the suicide rates among older adults. The emphasis should be placed on understanding the lived experiences of older individuals and tailoring programs accordingly.
Additionally, collaboration between researchers, healthcare providers, and policymakers can help translate research findings into practical, community-based applications. By prioritizing research that explores the intersection of mental health, social support, and aging, we can foster a deeper understanding of how to protect the mental well-being of older adults, ultimately steering efforts toward effective suicide prevention.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are effective suicide prevention strategies for older adults?
Effective suicide prevention strategies for older adults include increasing access to mental health resources for seniors, fostering community engagement to reduce loneliness, and promoting awareness of geriatric suicide prevention programs. Tailored interventions that address the unique mental health needs of seniors can significantly help in reducing suicide rates in this age group.
How can families support elderly loved ones facing suicide risk?
Families can support elderly loved ones facing suicide risk by maintaining open lines of communication, encouraging them to talk about their feelings, and connecting them with mental health resources for seniors. Recognizing signs of depression or isolation and utilizing online resources for older adults can also be pivotal in providing the needed support and intervention.
What role does loneliness play in elderly suicide risk?
Loneliness is a significant factor in elderly suicide risk, as it can lead to depression and a feeling of hopelessness among seniors. Understanding the impact of loneliness on mental health emphasizes the need for geriatric suicide prevention initiatives that focus on social connections and community interactions to combat isolation.
Are there online resources available for older adults struggling with suicidal thoughts?
Yes, there are online resources available for older adults struggling with suicidal thoughts. Websites dedicated to mental health resources for seniors offer valuable information, support groups, and crisis hotlines tailored specifically for the elderly population, addressing their unique concerns and facilitating access to help.
What are common signs of suicidal ideation in older adults?
Common signs of suicidal ideation in older adults include expressing feelings of hopelessness, withdrawing from friends and family, drastic changes in behavior or mood, and discussing death or suicide. Being aware of these symptoms can help in early detection and geriatric suicide prevention efforts.
How can community programs aid in suicide prevention for older adults?
Community programs aid in suicide prevention for older adults by fostering social interaction, providing mental health resources, and creating supportive environments that encourage engagement. Programs that address loneliness and promote mental wellness can be effective in reducing the elderly suicide risk.
Why is there a lack of resources for suicide prevention aimed at older adults?
The lack of resources for suicide prevention aimed at older adults often stems from underrepresentation in research and systemic biases that overlook the needs of this population. This highlights the urgent need for increased funding and the development of specialized programs tailored to the elderly.
How can online mental health resources for seniors be improved?
Online mental health resources for seniors can be improved by making them more user-friendly, accessible, and tailored to the specific needs of older adults. Enhancements such as simplified navigation, relevant content on geriatric suicide prevention, and emotional support forums can make these resources more effective.
What organizations focus on geriatric suicide prevention?
Several organizations focus on geriatric suicide prevention, including the National Institute on Aging and local mental health nonprofits. These organizations work on increasing awareness, funding research, and developing programs that specifically target the mental health needs of older adults.
How important is research in addressing elderly suicide risk?
Research is crucial in addressing elderly suicide risk as it helps identify trends, risk factors, and effective prevention strategies. It provides the foundation for developing tailored interventions and increasing the visibility of issues affecting seniors, thereby improving suicide prevention efforts in this vulnerable population.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Older adults (75+) have the highest suicide rates (20.3 per 100,000). |
| Existing suicide prevention resources are not effectively targeted toward older adults. |
| McLean Hospital study reveals imbalance in online resources for this demographic. |
| Increasing internet use among seniors requires better resource accessibility. |
| Addressing social isolation and biases is crucial in suicide prevention efforts. |
| Calls for targeted campaigns and more research funding for older adults. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is an urgent need as this demographic faces the highest rates of suicide among all age groups. The recent study emphasizes the alarming lack of accessible resources designed specifically for older individuals, despite their increasing presence online. Efforts to improve suicide prevention must reflect the unique healthcare challenges faced by seniors, which include social isolation and a lack of representation in research. By increasing visibility and targeting resources effectively, society can better safeguard our older population against the tragedy of suicide.