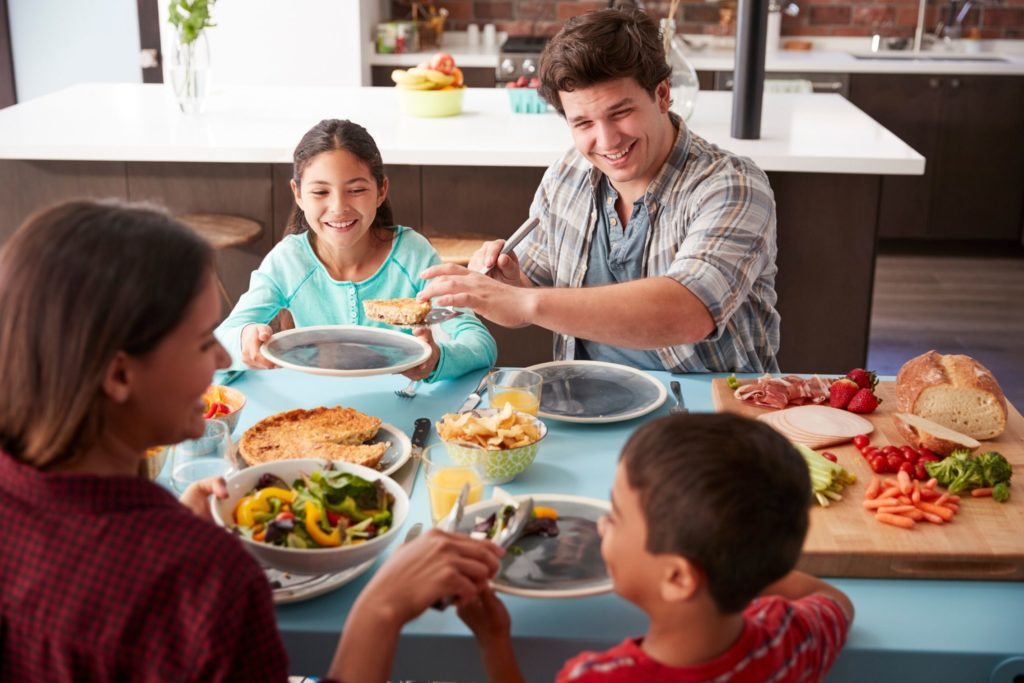
Shared meals and happiness are intricately linked, highlighting the profound impact that dining together can have on our emotional well-being. Research indicates that individuals who frequently enjoy meals with others report higher satisfaction levels and a greater sense of joy in their daily lives. A study featured in the World Happiness Report suggests that this social connection is as significant as income when it comes to predicting happiness levels across diverse demographics. However, trends revealed in the American Time Use Survey show a concerning rise in the number of people dining alone, which may contribute to lower happiness levels. As we explore the relationship between these shared experiences and our overall well-being, it becomes crucial to understand how meals can not only foster connection but also enhance our quality of life.
The dynamics of group dining and overall contentment unveil a fascinating aspect of human interaction. Engaging in communal meals serves not only as a nourishment ritual but also as a cornerstone of social ties that can elevate our emotional states. Frequent interaction at the dinner table may mitigate the risks associated with solitude, as evidenced by shifts in dining patterns noted in various reports, including the American Time Use Survey. The noticeable increase in solo dining raises questions about its effects on social well-being and individual happiness. Ultimately, embracing the practice of sharing food could play a pivotal role in enhancing our collective emotional health and fostering stronger community bonds.
The Correlation Between Shared Meals and Happiness
Research suggests a profound link between shared meals and heightened happiness levels. According to the World Happiness Report, individuals who regularly dine with others report increased satisfaction in life compared to those who often eat alone. This connection is attributed to the social interaction that comes with shared meals, which fosters a sense of belonging and enhances social connection, crucial factors that contribute to overall well-being.
As indicated by the American Time Use Survey, the trend shows a concerning rise in the number of individuals dining alone, climbing 53 percent since 2003. This decline in communal dining is particularly pronounced among younger generations, which could have lasting implications on their happiness levels and social skills. As shared meals often provide opportunities for meaningful conversations and connections, the reduction of these experiences may directly influence individual happiness.
Dining Alone: Trends and Implications
The rise in dining alone presents a significant challenge to societal norms that value communal eating as a source of joy and social connection. Data from the American Time Use Survey indicates that approximately 25% of Americans reported eating all meals alone in 2023, suggesting a considerable shift in social behavior. This increase is not just a statistical anomaly but represents a cultural shift towards more isolated lifestyles, which may adversely affect mental well-being and happiness levels.
Interestingly, while the act of dining alone may initially seem inconsequential, its broader implications could influence societal health metrics. Experts like Micah Kaats highlight the need for future research to explore how this trend correlates with other factors contributing to happiness. If shared meals are indeed as predictive of happiness as income, understanding the determinants behind the growing trend of eating alone could be essential in crafting interventions aimed at improving social connections and overall well-being.
The Role of Shared Meals in Social Connectivity
Shared meals can play a transformative role in enhancing social connection, which is intrinsically tied to happiness levels. Engaging in group dining experiences fosters relationships, encourages community bonding, and builds a support network that individuals can rely on. These interactions not only nourish the body but also nurture the soul, reinforcing the idea that happiness is significantly influenced by one’s social environment and meaningful interactions.
Moreover, the potential for reducing social isolation through shared meals is an area ripe for exploration. As we face increasing rates of mental health struggles, championing initiatives that emphasize communal dining can be pivotal in reconnecting communities. Encouraging families, friends, and even strangers to share meals may serve as a simple yet powerful intervention in combating loneliness and enhancing social cohesion, leading to improved happiness levels across all demographics.
Exploring Happiness Beyond Financial Indicators
Traditional metrics of happiness, such as income or employment status, often fall short in capturing the complete picture of well-being. The recent findings from the World Happiness Report challenge the paradigms of happiness measurement, proposing that the quantity of shared meals is a more reliable indicator of personal satisfaction. Unlike financial indicators, which can be subjective and variable, the frequency of shared dining experiences presents a tangible measure of an individual’s social interactions and overall happiness.
This shift in perspective prompts a reevaluation of how we assess happiness in society. It encourages researchers and policymakers to consider subjective measures like shared meals alongside conventional economic indicators. By doing so, they can develop holistic policies that address social connectivity and mental well-being, recognizing that true happiness often lies in the inextricable connections formed over a shared table.
Breaking Down the Statistics of Meal Sharing
The stark statistics from the American Time Use Survey illustrate a troubling reality: a significant portion of the population is increasingly dining alone. This shift poses critical questions about the implications of such a trend on societal well-being. With reported figures showing a 53% increase in solo dining since 2003, researchers are compelled to further investigate how this correlates with overall happiness and mental health outcomes.
Analyzing these statistics provides valuable insights into the changing dynamics of social interaction, emphasizing the importance of shared meals in maintaining social ties. It suggests that as people increasingly opt for solitary dining, they may inadvertently be compromising their happiness levels. This realization can spur initiatives aimed to rekindle the practice of communal meals, whether through community programs or informal gatherings, ultimately promoting better mental health outcomes.
Cultural Perspectives on Shared Meals and Happiness
Cultural narratives surrounding food often emphasize the importance of sharing meals as a communal activity that fosters happiness and connection. In many cultures, dining is more than just sustenance; it embodies customs, traditions, and social rituals that celebrate togetherness. Understanding how different societies value shared meals can shed light on the universal need for connection and its direct impact on happiness levels.
By examining various cultural practices related to communal dining, we can learn valuable lessons about the role of food in building relationships. For instance, cultures that prioritize family gatherings around the dinner table tend to exhibit higher measures of social cohesion and happiness. Therefore, embracing these cultural perspectives on sharing meals can enrich our understanding of happiness, potentially guiding us towards healthier, more socially connected lifestyles.
The Psychological Benefits of Dining Together
Psychological studies indicate that dining together can yield significant mental health benefits. Shared meals provide a platform for engaging conversations, laughs, and stories that are integral to building emotional resilience and fostering happiness. Groups that regularly engage in shared dining experiences often report lower levels of stress and anxiety, highlighting the therapeutic nature of communal meals.
Moreover, the infrastructural implications of shared meals extend into the realm of public health. By encouraging dining together, we not only hopefully nourish our bodies but also cultivate supportive communities. The psychological uplift derived from shared meals can be instrumental in recent efforts to combat social isolation, promoting policies that advocate for community dining events and experiences as a foundation for mental wellness.
Future Research Directions: Meals as a Well-being Indicator
As the conversation surrounding shared meals and happiness evolves, the need for rigorous research becomes increasingly apparent. Future studies should seek to clarify the causality between shared meals and increased happiness levels. For instance, researchers could explore whether the act of sharing meals leads to improved mental health or if happier individuals naturally engage in more social dining experiences, bridging the gap between correlation and causation.
Moreover, expanding research to include diverse populations and varying cultural contexts will provide a more comprehensive understanding of the relationship between meal sharing and happiness. By examining these variables, we may uncover innovative approaches to utilizing shared meals as a public health strategy, aiming to enhance social connections and ultimately improve mental health outcomes across various demographics.
Community Initiatives for Promoting Shared Meals
Understanding the importance of shared meals as a facilitator of happiness encourages the development of community initiatives focused on promoting communal dining experiences. Programs that organize potlucks, group dinners, or neighborhood cookouts can act as catalysts for social integration and strengthen community bonds, simultaneously improving social connection and happiness levels within the community.
Creating spaces where communal dining is celebrated not only mitigates the rise of social isolation but also fosters a culture of togetherness. By investing in community meal initiatives, policymakers can directly tackle the issues highlighted by the American Time Use Survey, encouraging citizens to engage with one another, share stories, and cultivate the important human interactions that lead to increased overall happiness.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do shared meals impact happiness levels according to recent studies?
Recent studies, including findings from the World Happiness Report, indicate that shared meals significantly enhance happiness levels. People who frequently dine with others report higher life satisfaction and positive emotions, suggesting that social connections fostered during shared meals play a crucial role in overall well-being.
What does the American Time Use Survey reveal about dining alone and its effect on social connection?
The American Time Use Survey shows a growing trend of Americans dining alone, with about 1 in 4 individuals reporting solitary meals. This rise in solitary dining is concerning as it correlates with lower social connections, which can detract from happiness and well-being.
Is dining alone detrimental to one’s happiness?
While dining alone isn’t inherently unhappy, studies suggest that shared meals promote social bonds and enhance happiness. The absence of these connections from shared meals may contribute to feelings of isolation, impacting overall life satisfaction.
What factors are considered more predictive of happiness: shared meals or income?
Research, as cited in the World Happiness Report, indicates that the number of shared meals is comparably predictive of happiness as income. This correlation suggests that meaningful social interactions such as shared meals can sometimes have a more profound impact on well-being than financial status.
Can sharing meals be a potential intervention for improving mental health?
Yes, increasing shared meals could serve as an effective intervention for improving mental health and well-being. By encouraging more social dining experiences, policymakers could address issues of social isolation and promote higher happiness levels among individuals.
How do social connections from shared meals influence well-being?
Social connections formed through shared meals create environments where individuals can engage, support each other, and share positive experiences. This interaction is essential for enhancing happiness levels and fostering a sense of belonging in communities.
What are the implications of declining shared meal times in society?
The declining frequency of shared meals, as highlighted by the American Time Use Survey, suggests increasing social isolation, which may negatively affect community ties and overall happiness levels. Addressing this downward trend may be crucial for enhancing well-being and social connection.
How can I encourage more shared meals to boost happiness in my community?
To foster more shared meals in your community, consider organizing potlucks, community dinners, or family gatherings. Creating a culture that values social dining can strengthen connections and enhance happiness among participants.
What role does cultural context play in shared meals and happiness?
Cultural context greatly influences the significance of shared meals. In many cultures, communal dining is a celebrated tradition that reinforces social bonds and enhances happiness levels. Understanding these cultural dynamics can inform how shared meals contribute to well-being globally.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Shared Meals and Happiness | Shared meals are a strong indicator of happiness, possibly even more so than income. |
| Statistical Insight | 1 in 4 Americans reported eating all meals alone in 2023, marking a 53% increase since 2003. |
| Demographics Impact | The trend of dining alone affects all age groups, with the most significant decline in younger populations. |
| Research Correlation | The study highlights a crucial link between the frequency of shared meals and happiness, although it doesn’t clarify causation. |
| Challenges in Measurement | Happiness is often hard to measure compared to the straightforward nature of meal sharing queries. |
| Future Implications | The results suggest potential policy interventions focused on promoting shared meals to enhance well-being. |
Summary
Shared meals and happiness are intricately linked, as recent research suggests. Eating meals with others not only correlates with greater life satisfaction but may also serve as a viable alternative measure of well-being compared to traditional metrics like income. With the alarming rise in solitary dining reported in the U.S., it becomes crucial to foster communal eating experiences to enhance overall happiness. Policymakers and researchers should prioritize initiatives encouraging shared meals to combat social isolation and improve mental health outcomes.